Pancreatic cancer is an aggressive disease with early spread being common. Once it metastasizes beyond the pancreas, the prognosis worsens. Knowing the signs of metastatic pancreatic cancer helps in timely diagnosis and management.
Signs that pancreatic cancer has spread
Some common indicators that pancreatic cancer may have metastasized include:
- Weight loss and loss of appetite due to tumor burden and metabolic changes
- Fatigue due to anemia from tumor bleeding
- Pain in abdomen, back or other areas of the body where cancer has spread
- Jaundice and light-colored stools as tumor obstructs bile duct
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal swelling from tumor blockage
- Enlarged lymph nodes in neck, armpit and groin
- Lumps under the skin
- Bone pain or fractures without trauma
- Neurological symptoms like back pain due to spinal metastases
- Digestive issues like diarrhea or constipation
- Blood clots in legs or lungs
- Chest pain and shortness of breath from lung metastases
- Enlarged liver or spleen on exam if these organs are affected
RELATED : What cancer causes jaw and ear pain?
How likely is pancreatic cancer to spread?
Nearly 80% of pancreatic cancer patients have metastasis at diagnosis, making it a highly aggressive disease. The local invasion and early spread are fueled by lack of early symptoms. By the time of detection, the tumor has generally already spread to surrounding tissues, blood vessels and distant organs.
Where does pancreatic cancer usually spread to first?
The major sites of first metastases are liver and peritoneal cavity/ascites in over 90% cases. Other frequent sites are lymph nodes, lungs, bones and brain. The disease most often follows a pattern of local spread to adjacent tissues and abdominal structures, then via circulation to liver, followed by formation of tumor deposits (carcinomatosis) in the abdomen and chest cavity.
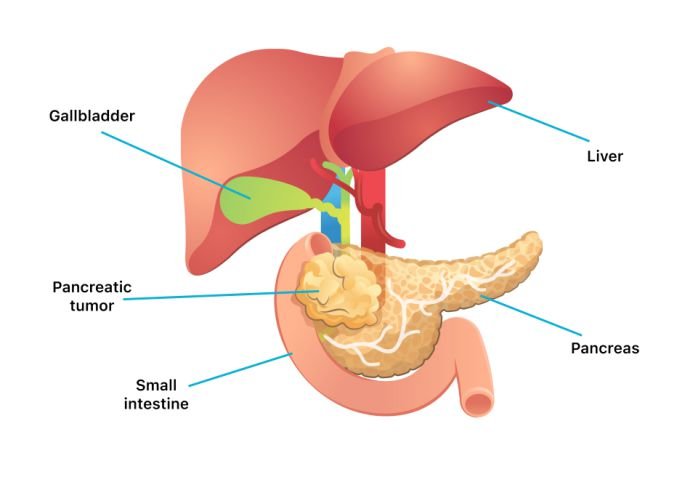
Signs that pancreatic cancer has spread to liver
Liver is the most common site of first metastasis from pancreatic cancer. Signs that pancreatic cancer has spread to liver may include:
- Enlarged liver that feels firm or nodular on palpation
- Abdominal discomfort or pain in the right upper region
- Jaundice from obstruction of bile ducts within the liver
- Nausea, loss of appetite, weight loss
- Abdominal swelling due to ascites
- Lab tests show elevated liver enzymes and bilirubin levels
- CT/MRI scans detect multiple liver lesions characteristic of secondary tumors
Does pancreatic cancer spread quickly?
Yes, pancreatic cancer is considered rapidly progressing. Most spread occurs within the first two years when tumors silently invade adjacent tissues and distant organs. Prognosis drops significantly once metastases are detected. The average survival rates for metastatic pancreatic cancer range between 3-11 months. Factors like tumor load, location and aggressiveness determine individual speed of spread.
How is pancreatic cancer that has spread treated?
Once spread occurs, the goal shifts from cure to palliation. Patients receive chemotherapy, targeted drugs or immunotherapy based on molecular profiles and performance status. In select cases with limited metastases, surgical resection or localized ablation therapies like cryotherapy or radiofrequency heat ablation may provide benefit along with chemo. Radiation and pain management also help improve quality of life. Palliative care addresses physical, psychological and spiritual needs. Clinical trials evaluate new combinations.
Metastatic pancreatic cancer survival rate
The average survival period after diagnosis ranges from 3-11 months depending on spread extent and treatment received. Around 14% of patients survive up to 1 year while only 3% survive over 5 years. Some factors indicating better prognosis include:
- Good functional status and minimal weight loss at diagnosis
- Localized metastases limited to one organ like liver
- Good response to initial chemotherapy
- Ability to undergo metastatic tumor removal
- Targeted therapies for specific mutations
- Participation in clinical trials of new drugs
Pancreatic cancer has a propensity for metastases even at an early stage. Being aware of warning signs helps detect spread and optimize supportive care. While cure is often not possible once spread occurs, prompt multi-disciplinary management can still improve length and quality of life significantly.
Read Next : How long can you live with bladder cancer stage 4








Discussion about this post